Earthquake Early Warning Gets Big Boost In New Federal Budget
Listen
An earthquake early warning system under development for the West Coast gets a major boost in the new federal budget that President Donald Trump signed into law Friday.
President Trump’s original budget proposal for 2018 zeroed out funding for earthquake early warning. But Congress dramatically reversed that. The new federal budget increases spending to build a warning system to $23 million this year, more than double the $10 million that the U.S. Geological Survey got for this last year.
UC Berkeley seismologist Richard Allen said the budget boost keeps the system on track for a “limited” public rollout late this year.
“Thinking about warning times, we’re talking about seconds, tens of seconds. The best case scenario is a few minutes,” Allen said. “We should be thinking about how we can react with warnings of a few seconds.”
The system designers say a short advance warning could be used to open fire station doors, slow down trains, pause surgeries or stop and open elevators at the next floor.
Down the road, the general public will be able to get alerts to drop, cover and hold on via a smartphone app, TV screens and other connected devices.
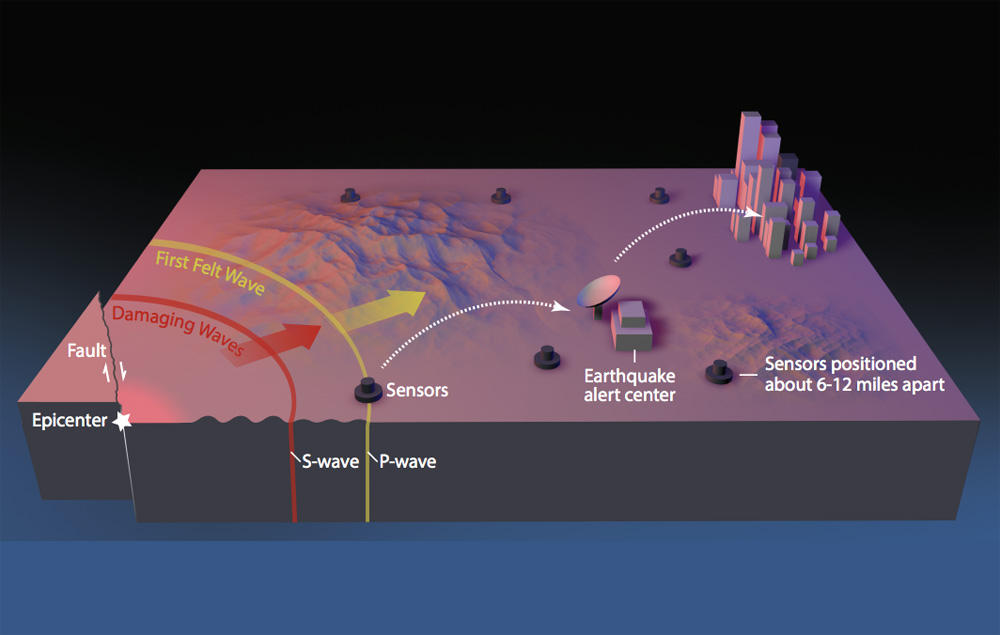
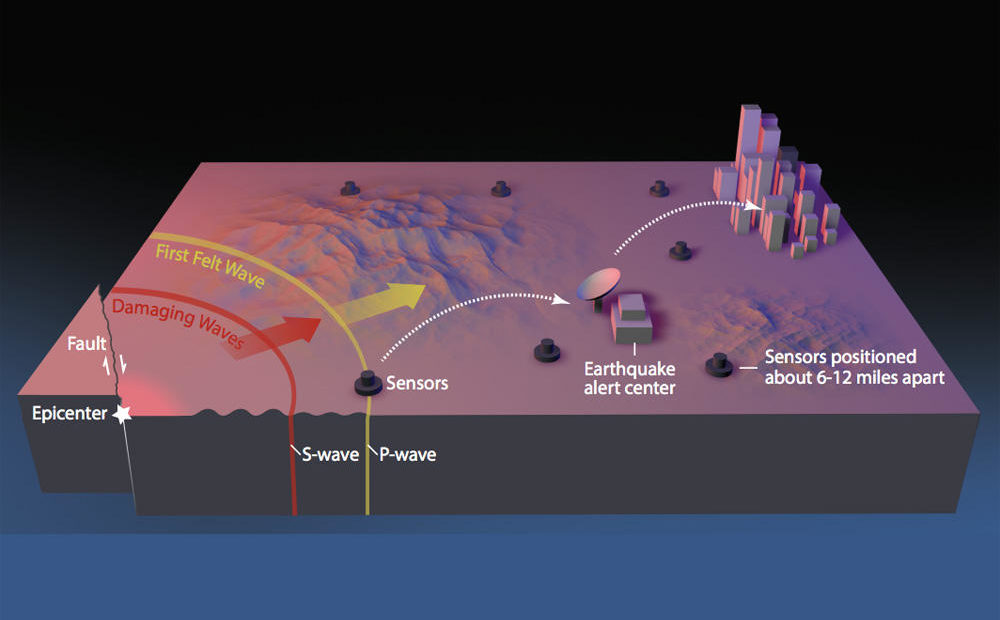
Allen said the new funding for the earthquake warning system will pay for things like additional sensors and for fine tuning the software to automatically detect damaging quakes and issue alerts. At this point, the system has about half of the desired seismic stations in place, which will eventually encompass a wide network of more than 1,000.
USGS and partner institutions including the Pacific Northwest Seismic Network, University of Washington, University of Oregon and UC Berkeley have trademarked the name ShakeAlert. The prototype has successfully alerted researchers to moderate earthquakes before shaking reached their locations.
A social science committee continues to study and tweak the interface to figure out how best to convey a useful warning and educate users to respond appropriately.
“The (prototype) system is running very well in regions that have stations that are pretty dense already, which is primarily the urban areas up and down the West Coast,” Allen said. “I’m very excited about the possibility of the limited public rollout later this year. I think the greatest challenge frankly, is fear of screwing up.”
“The system might make a mistake and people are very concerned about that,” Allen explained. “It is good to recognize that, but I think we really have to get past this.”
Allen said the early warning systems already in service in other countries such as Mexico are imperfect too.
“What we have learned from Mexico is that the receivers of the information, the public, they understand that there are technical limitations to these systems. They recognize that the system is not perfect, but they still see it as being valuable.”
Allen spoke during a webinar hosted by the National Academies of Sciences, Engineering and Medicine on Friday.
During the same event, University of Oregon seismologist Diego Melgar described a goal of adding accurate tsunami prediction and warning capabilities to the emerging ShakeAlert warning system.
“I think overall the outlook is quite positive,” Melgar said. “With continued effort for Cascadia, we will have warnings for tsunamis in under five minutes.”
Melgar added a caveat that real-time tsunami modeling using very sensitive GPS and ground motion sensors on land will always be somewhat uncertain. The U.S. national tsunami warning centers currently use offshore buoys and supercomputer models to assess tsunami hazards and issue advisories over broadcast channels and NOAA weather radios.
Copyright 2018 Northwest News Network
Related Stories:

Concert in Pasco To Raise Disaster Relief Funds For Colima in Mexico
The Mid-Columbia Symphony will perform a public concert this September 24th in Pasco at 6:00 p.m. Photo from Mike Gonzalez reports website. Listen (Runtime 0:53) Read A symphonic concert will
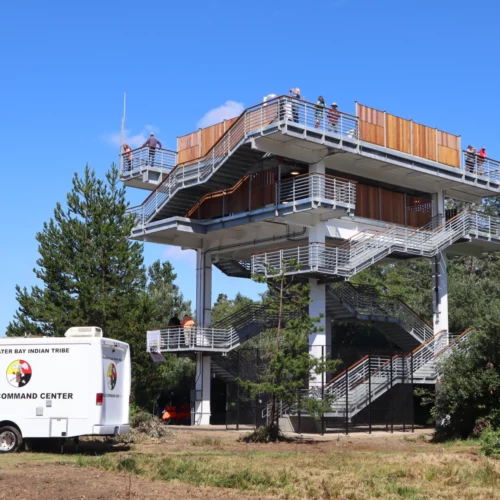

Coastal Washington Tribe Creates Higher Ground By Building Tsunami Tower, First Of Its Type Here
There is a new option to escape a tsunami if you’re on the southwest coast of Washington when the Big One strikes. The Shoalwater Bay Indian Tribe on Friday dedicated a 50-foot tall evacuation tower in Tokeland, Washington. Tribal leaders and the Federal Emergency Management Agency said the new tsunami refuge platform should be an example and inspiration for other vulnerable coastal communities.
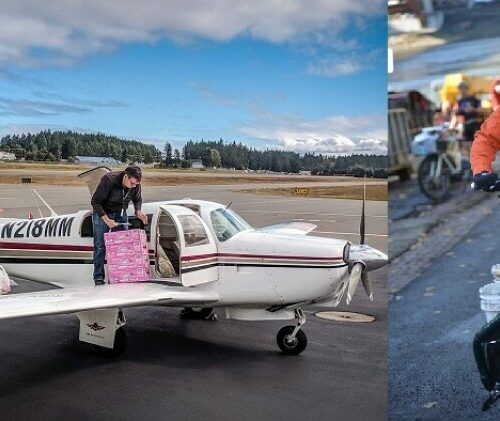

By Air And By Bike, Civilian Pilots And Cyclists Rehearse Delivering Aid After ‘The Big One’
A huge dress rehearsal for regional earthquake disaster relief was supposed to happen next week until the ongoing pandemic forced its cancellation. The scrubbed Cascadia Rising exercise would have involved more than 22,000 participants – chiefly U.S. soldiers, sailors and airmen as well as state, local and tribal emergency planners. Some smaller drills are going ahead this weekend and next featuring civilian volunteers who will demonstrate unusual ways aid may get to Pacific Northwest earthquake survivors.