Welcome To Klickitat Canyon, South-Central Washington’s New Conservation Area
READ ON
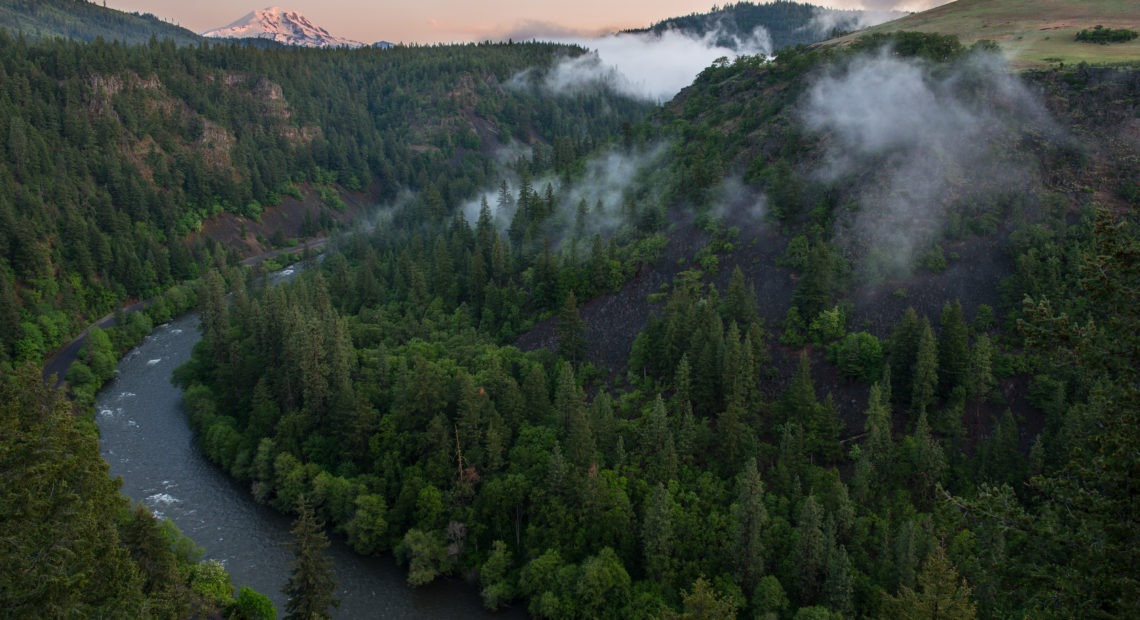
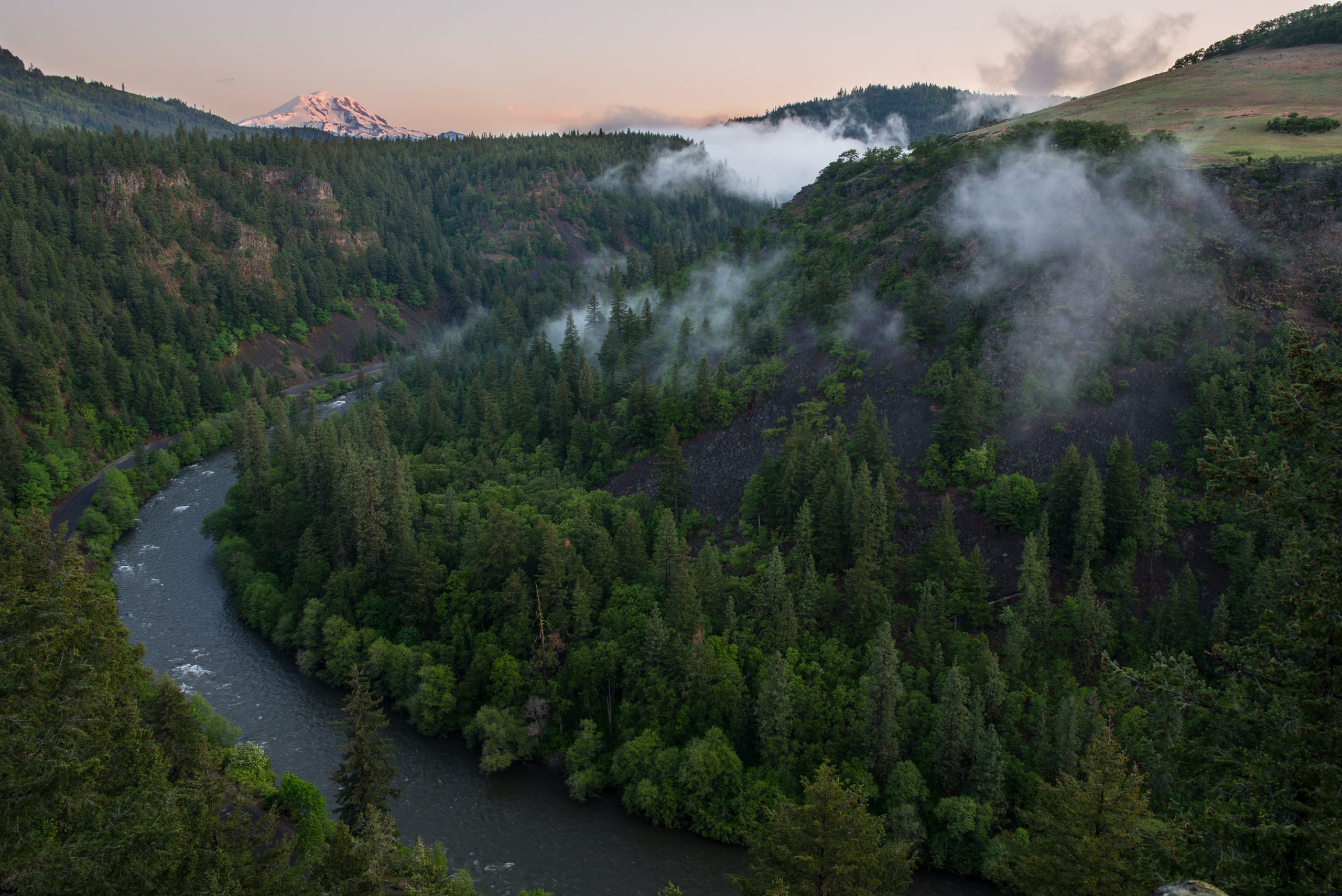
Mountain goats, mule deer and black bears all move across the rugged basalt cliffs, forest and grasslands that make up the Klickitat Canyon Conservation Area. Salmon and steelhead swim up the Klickitat River, Washington’s longest wild river, running through the conservation area.
The newly completed conservation area in south-central Washington is expected to protect habitat and lead to a more resilient forest. Conservation groups say this is a big step toward connecting important ecosystems in the area.
“Comprehensive conservation gives (wildlife) the space and the varied landscapes they need to thrive,” Jay Kosa, the Columbia Land Trust spokesperson, said.
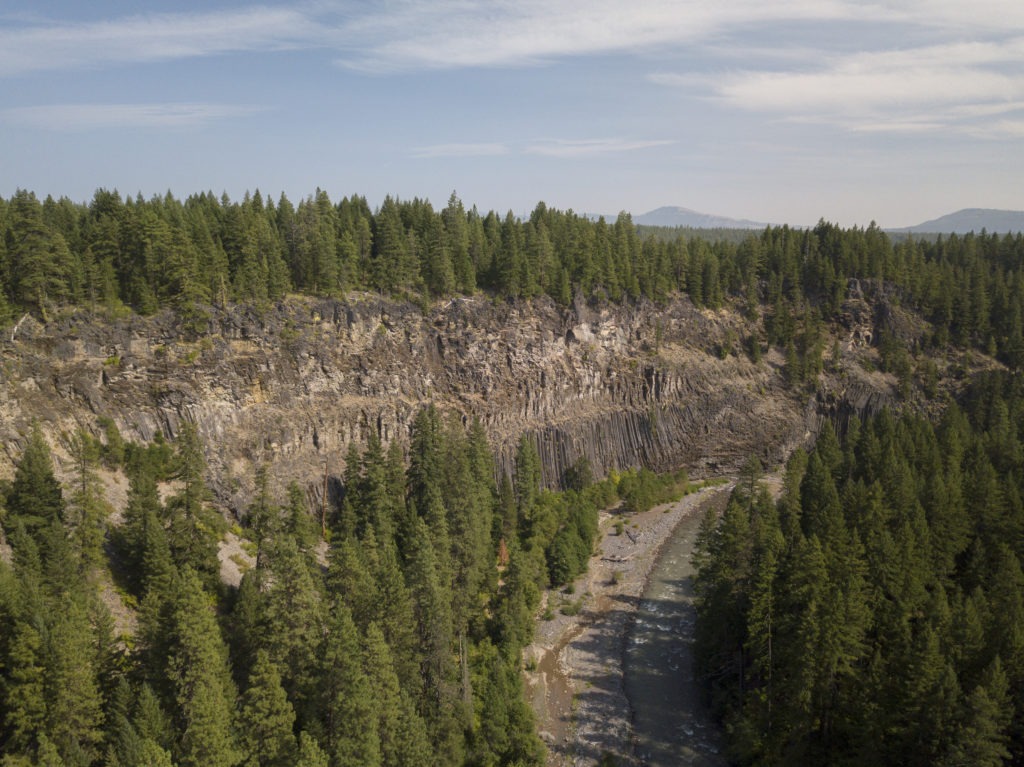

The Klickitat Canyon Conservation Area will connect 11,000 acres of wildlife habitat in south-central Washington. Courtesy of Columbia Land Trust
Kosa said it took around 12 years, but the conservation organization has now acquired around 11,000 acres to connect public and tribal conservation lands.
The Yakama Nation supported the completion of the conservation area, which lies within its ancestral lands.
“It is important to share the understanding of the importance of enhancing and protecting these significant aquatic and ecological places because a watershed like the Klickitat is the last of its kind,” Yakama Nation Natural Resources Superintendent Phil Rigdon said in a news release.
Kosa said this conservation area will help bridge gaps in the ecosystem.
“If it were to be developed or fragmented by being sold into parcels, it would really interrupt the ability for wildlife to move across the landscape,” Kosa said.
Columbia Land Trust Forest Conservation Director Cherie Kearney says land connectivity will help wildlife adapt to a changing climate. It gives them easier access to higher elevations as temperatures warm.
“As the temperature warms, there can be places that have gradient, they have topography and diversity, allowing animals to spread out a little bit, incrementally toward new habitat,” Kearney said.
She said the groups will start to manage the area to create forestry jobs and make the area more resistant to wildfire. Kearney said the group will harvest timber more for “conservation forestry,” which includes thinning and some revenue harvest.
“It’ll all be balanced toward creating an older, bigger forest,” she said.
Related Stories:

Officials clash over North Cascade grizzly bear reintroduction
A grizzly bear in Yellowstone National Park. (Credit: U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service) Listen (Runtime 1:22) Read In a recent heated committee hearing on Capitol Hill, U.S. Rep. Dan Newhouse,

Volunteers helping sagebrush, wildflowers grow where fires burned
Volunteers with the Columbia Basin chapter of Washington’s Native Plant Society met up at a local hiking hotspot in southeastern Washington on a cold November afternoon to replant sagebrush tubelings

Tribal members gather to demand U.S. Government fulfill treaty obligations
Sockeye salmon like these are among the salmon species in peril. (Credit: Aaron Kunz) Listen (Runtime 2:57) Read For Northwest tribes, removing the four lower Snake River dams means more